Usability Testing
“Product managers must balance the needs of customers, the capabilities of technology, and the goals of the business.”
– Ken Norton
Welcome to Day 11 of the PM series – Product Management in 30 days!
Product management is a multifaceted discipline, demanding a keen understanding of customer needs, a strategic mindset, and an unwavering commitment to product excellence. One of the most indispensable tools in the product manager’s arsenal is Usability Testing and Feedback.
This extensive post will explore the crucial role of usability testing and feedback in product development, highlighting best practices, common pitfalls, and strategies for optimizing the process.
Learning Objectives
- Understanding the Significance of Usability Testing: Identify the shift in focus from product delivery to user experience in modern product development. Comprehend the role of usability testing in aligning products with user expectations and refining them for optimal performance.
- Exploring Usability Testing Objectives: Recognize the primary objectives of usability testing, including issue detection, enhancement possibilities, and gaining insights into user behaviour and preferences. Understand how usability testing contributes to creating user-centric products.
- Key Elements of Usability Testing: Familiarize yourself with the crucial elements of usability testing, including the facilitator, tasks, and users. Understand the role and skills required for an effective facilitator, the types and purposes of tasks, and the importance of diverse user representation.
- Types of Usability Testing Methods: Gain insights into various usability testing methods, such as moderated usability testing, unmoderated remote usability testing, thinking-aloud testing, and others. Understand the specific use cases for each testing method and their advantages in different scenarios.
- Usability Testing Process and Leveraging User Feedback: Explore the steps involved in the usability testing process, from planning and participant recruitment to conducting tests, analyzing results, and iterative improvement. Learn strategies for collecting, categorizing, prioritizing, and implementing user feedback to drive continuous product enhancement.
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of product development, the emphasis has shifted from merely delivering products to the market to creating exceptional user experiences. Usability testing and feedback are integral components of this journey, as they empower product managers to align their offerings with user expectations, identify pain points, and fine-tune their products to perfection.
👨🔬 Why Usability Testing?
The objectives of usability testing can differ from one study to another, but they typically encompass:
- Detecting issues within the design of the product or service
- Discovering possibilities for enhancement
- Gaining insights into the behaviour and preferences of the target users
The key elements of usability testing include the facilitator, tasks, and users. Here’s an overview of each element:
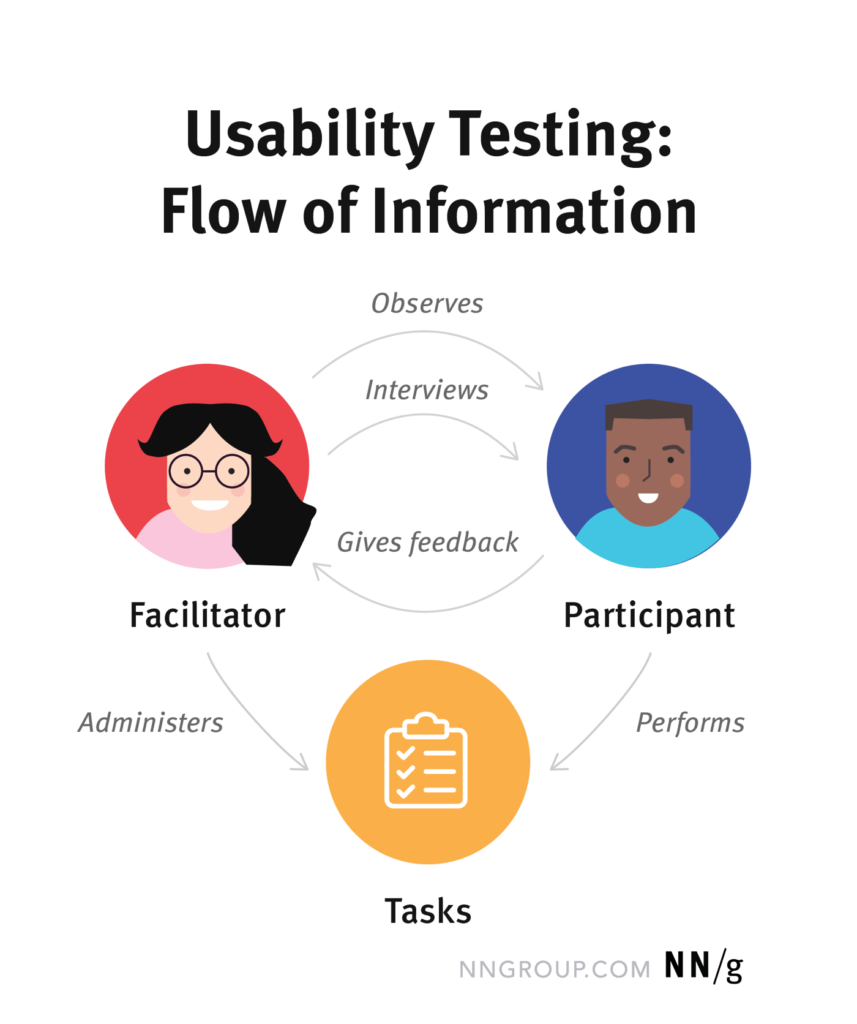
Facilitator:
- Role: The facilitator is responsible for guiding the usability testing session, interacting with participants, and collecting valuable data. They play a crucial role in creating a comfortable environment for users, providing instructions, and asking probing questions to gather insights.
- Skills: Effective communication, empathy, the ability to remain neutral, and a good understanding of the testing goals are essential skills for a facilitator. They should be able to adapt the session based on user reactions and responses.
Tasks:
- Description: Tasks are the specific activities or scenarios that participants are asked to perform during the usability testing session. These tasks are designed to simulate real-world interactions with the product and help assess its usability.
- Types of Tasks: Tasks can vary, including basic navigation, completing specific actions, locating information, or using particular features. They are carefully crafted to align with the goals of the usability test and evaluate different aspects of the product.
Users / Participant:
- Selection: Users represent the target audience or user personas for the product. They should reflect the diversity of the actual user base. Usability testing can involve a range of users with varying levels of experience and familiarity with the product or similar products.
- Recruitment: Participants are typically recruited based on specific criteria to ensure the testing provides relevant insights. This may include demographics, expertise levels, or specific user behaviours.
Three Key Interactions:
- Introduction: The facilitator introduces the purpose of the usability test, establishes rapport with the user, and provides any necessary instructions.
- Task Execution: Users perform the assigned tasks while the facilitator observes and records their interactions. Users may also be encouraged to “think aloud” to express their thoughts and feelings.
- Feedback Collection: After each task or at the end of the session, the facilitator gathers feedback from users. This may involve asking about their experience, perceived challenges, and suggestions for improvement.
👨🔬 Types of Usability Testing
Usability testing encompasses various methods to evaluate how well users can interact with a product and accomplish specific tasks. Here are some common types of usability testing:
Moderated Usability Testing:
- Description: A facilitator guides participants through a series of tasks while observing and collecting data. The facilitator can ask questions and gather qualitative insights during the session.
- Use Case: Ideal for in-depth understanding and gathering detailed feedback. Commonly used in early stages of product development.
Unmoderated Remote Usability Testing:
- Description: Participants complete tasks independently at their own locations using a remote testing platform. Participants’ interactions are recorded, and feedback is collected asynchronously.
- Use Case: Suitable for testing with a geographically diverse user base. Efficient for quick feedback on specific tasks or features.
Thinking-Aloud Testing:
- Description: Participants verbalize their thoughts and feelings while interacting with the product. This method provides insights into users’ cognitive processes and decision-making.
- Use Case: Effective for understanding the reasoning behind user actions and identifying potential usability issues.
Hallway Testing (Guerrilla Testing):
- Description: Informal testing conducted with individuals who are not part of the target audience. Testers often approach people “in the hallway” or in public spaces for quick feedback.
- Use Case: Useful for quick and informal feedback, especially in situations where recruiting specific participants is challenging.
A/B Testing (Split Testing):
- Description: Involves comparing two versions of a webpage or interface (A and B) to determine which performs better. Users are randomly assigned to either version, and their interactions are measured.
- Use Case: Commonly used for optimizing specific elements, such as layouts, colours, or call-to-action buttons, by measuring quantitative metrics like conversion rates.
First Click Testing:
- Description: Focuses on the first click users make when presented with a specific task. It helps assess the intuitiveness of navigation and whether users can find information quickly.
- Use Case: Useful for evaluating the effectiveness of navigation menus and the clarity of the user interface.
Accessibility Testing:
- Description: Evaluates how accessible a product is to users with disabilities. This includes testing for compliance with accessibility standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
- Use Case: Important for ensuring inclusivity and compliance with legal requirements related to accessibility.
Five-Second Tests:
- Description: Participants are shown a design for a very brief period (usually five seconds) and then asked questions about what they remember. This method assesses the immediate impact and clarity of a design.
- Use Case: Useful for evaluating the visual impact of landing pages, advertisements, or other designs.
These usability testing methods can be selected based on the specific goals, resources, and constraints of a given project. Often, a combination of these methods may be employed for a more comprehensive evaluation of a product’s usability.
👨🔬 Understanding Usability Testing
Usability testing is the process of evaluating a product by testing it with real users to uncover usability issues, gather feedback, and ensure that the product meets users’ needs and expectations. This methodology involves the following key steps:
1️⃣ Planning Usability Tests:
- Define clear objectives for the usability test.
- Identify the target user group or persona.
- Develop test scenarios and tasks that users will perform.
- Create a usability testing plan with timelines and resources.
2️⃣ Recruiting Participants:
- Select representative users who match the target audience.
- Ensure a diverse pool of participants to capture various perspectives.
3️⃣ Conducting the Test:
- Facilitate the usability test, guiding participants through tasks.
- Observe and record user interactions and feedback.
- Encourage participants to think aloud, expressing their thoughts and emotions.
4️⃣ Analyzing Results:
- Review test data and observations to identify usability issues.
- Categorize issues by severity, prioritizing critical ones.
- Use usability testing tools and software for efficient analysis.
5️⃣ Iterative Improvement:
- Implement design changes based on the findings.
- Repeat usability testing cycles to validate improvements.
- Continuously refine the product until it achieves optimal usability.
🔗 Leveraging User Feedback
User feedback is a treasure trove of insights that guide product improvements and innovation. It can come from various sources, including customer support, surveys, social media, and direct user interactions. To harness the power of user feedback effectively:
1️⃣ Collecting Feedback:
- Provide easy and accessible channels for users to submit feedback.
- Use surveys, feedback forms, and in-app feedback mechanisms.
- Encourage customer support teams to document and share user comments.
2️⃣ Categorizing and Prioritizing:
- Organize feedback into categories (bugs, feature requests, suggestions).
- Prioritize feedback based on impact, frequency, and alignment with product goals.
3️⃣ Analyzing and Triaging:
- Evaluate feedback to understand the root causes and context of issues.
- Prioritize feedback that directly affects usability and customer satisfaction.
4️⃣ Implementing Improvements:
- Translate feedback into actionable tasks for the development team.
- Monitor progress and provide updates to users who contributed feedback.
5️⃣ Closing the Feedback Loop:
- Notify users when their feedback leads to positive changes.
- Encourage a sense of ownership and collaboration with users.
😱 Common Pitfalls in Usability Testing and Feedback
While usability testing and feedback are essential, pitfalls can hinder their effectiveness:
- Bias in Testers: Testers may unintentionally influence participants or interpret their actions subjectively.
- Small Sample Sizes: Limited test participants may not represent the entire user base.
- Ignoring Negative Feedback: Focusing only on positive feedback can lead to missed opportunities for improvement.
- Not Closing the Loop: Always update users on changes based on their feedback to maintain trust.
- Overreacting to Feedback: Making hasty changes without thorough analysis can lead to new issues.
🖐️ Five Strategies for Success
To succeed with usability testing and feedback:
- Be User-Centric: Keep users at the centre of your product development process.
- Maintain Objectivity: Minimize bias in usability testing and approach feedback with an open mind.
- Iterate Continuously: Usability testing and feedback should be an ongoing process, not a one-time event.
- Educate Your Team: Ensure everyone understands the value of user feedback and usability testing.
- Prioritize Accessibility: Consider the needs of all users, including those with disabilities.
🔔 Conclusion
Usability testing and feedback are cornerstones of exceptional product management. They provide a roadmap to enhance user experiences, optimize product functionality, and foster a loyal customer base. By incorporating these practices into your product development lifecycle, you’re not just building products but crafting solutions that resonate with your audience and drive success.
Quiz Time
Question: What is the primary role of a facilitator in usability testing?
A. Develop test scenarios
B. Collect feedback from users
C. Guide the usability testing session
D. Analyze test data
Question: What is the purpose of thinking-aloud testing in usability evaluation?
A. Assessing visual aesthetics
B. Understanding cognitive processes and decision-making
C. Conducting tests remotely
D. Evaluating accessibility
Question: Which usability testing method is ideal for quick and informal feedback from individuals not part of the target audience?
A. Moderated usability testing
B. Unmoderated remote usability testing
C. Hallway testing (Guerrilla testing)
D. A/B Testing (Split Testing)
Question: What is the key advantage of unmoderated remote usability testing?
A. In-depth understanding
B. Efficient for quick feedback on specific tasks or features
C. Real-time collaboration
D. Detailed preview of the final product
Question: Why is it important to close the feedback loop in usability testing?
A. To avoid negative feedback
B. To minimize bias in testing
C. To maintain trust with users and update them on changes
D. To focus only on positive feedback
✍️ Write your answers in the comment section. e.g 1-a, 2-b, 3-c etc.
If you want to learn more about product management, you can also find other posts. The Full series is available here
One of the recommended books to learn about product management is Zero to One by Peter Thiel
💌 Do drop me a comment below if you found the content useful and/or want me to write on a specific topic. This will make my day! 🙂
Also, share the post if you think this might help someone. The sharing link is at the top of the page.
Join FreeMentor as a student if you are a newbie in product management and want to have one Free 1:1 mentorship session.
Disclaimer:
Please note that I don’t make any guarantees about the information supplied in this post. I share educational and informational resources that are intended to help you succeed in understanding product management. You nevertheless need to know that your ultimate success or failure will be the result of your own efforts, your particular situation, and innumerable other circumstances beyond my knowledge and control.
#ProductManagement #UsabilityTesting #UserFeedback #ProductDevelopment #UXDesign #LinkedInPost #ProductManager

